Samyama An Advanced Meditation Technique
Samyama is introduced in the third chapter (Vibhuti Pada) of the Yoga Sutras, specifically in Sutras 3.1 to 3.6.
 |
| Samyama - A Meditation Technique |
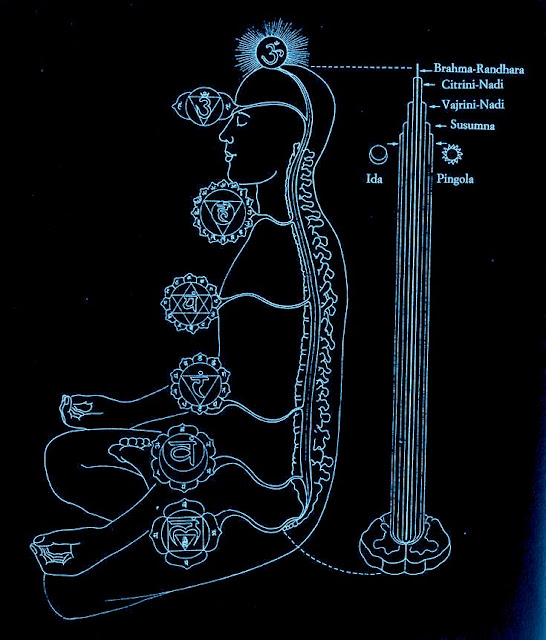
Samyama refers to a set of advanced meditation techniques that involve the simultaneous application of Dharana (concentration), Dhyana (meditation), and Samadhi (absorption or union) on a specific object, idea, or aspect of reality. It is considered a profound practice that can lead to deep spiritual insights and transformation.
Here are the steps of Samyama -
1. Dharana (Concentration) - In this first stage, you focus your mind intensely on a chosen object or concept. This requires sustained attention and the ability to exclude all other distractions from your awareness. The object of concentration could be an external object, an internal sensation, a mantra, or even an abstract idea.
2. Dhyana (Meditation) - Once you have achieved a deep and unwavering concentration on the chosen object, it naturally transitions into meditation. In this stage, you maintain your focus on the object without any effort. The distinction between the subject (meditator) and the object of meditation begins to blur.
3. Samadhi (Absorption) - Samadhi is the deepest stage of Samyama. Here, the practitioner and the focus of the meditation merge into one. The distinction between the observer and the observed dissolves, and the meditator experiences a profound sense of unity or oneness with the chosen object or concept. This state is often described as a state of profound bliss, transcendence, or enlightenment.
The origins of Samyama can be traced back to the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, a sage who lived around 200 BCE. The Yoga Sutras are a compilation of aphorisms that provide guidance on the practice of yoga, including its philosophical underpinnings and various techniques to attain spiritual realization and liberation (moksha).
Patanjali's Yoga Sutras have been highly influential in the development of yoga and meditation practices in India and around the world. Samyama is considered an advanced practice and is typically undertaken by experienced yogis who have mastered the preceding stages of yoga, including ethical principles (Yamas and Niyamas), physical postures (Asanas), breath control (Pranayama), and concentration (Dharana).
-Tanmay Bhati








Comments
Post a Comment
If there is any topic, do write us or mention in the comment box, in our next article we will definitely try to get on that.